The 3D printer is a machine that we hear more and more about on a daily basis and which is about to invade the traditional industry, but above all, to create a new type of industry: the collaborative industry also called Makers.
The 3D printer is a machine that we hear more and more about on a daily basis and which is about to invade the traditional industry, but above all, to create a new type of industry: the collaborative industry also called Makers.
So, how does a 3D printer work and why is it as revolutionary as it is claimed?
- The principle of 3D printing
- The main types of 3D printing
- How is a 3D printing machine controlled?
- The 3D printing process in images example in jewelry
- The costs of a 3D printer
The principle of 3D printing
First of all, it should be understood that 3D printing is an additive manufacturing process, unlike conventional manufacturing processes which are subtractive.
A carpenter creates a functional piece of wood by removing material from a block of solid wood. Just as a machinist will create a metal part by machining a piece of metal larger in volume and weight than the final part.
Unlike these processes, 3D printing works by localized addition of material to create only the final functional part. There is almost no loss of raw material (apart from the supports).
Concretely, how do 3D printing machines work?
To manufacture a physical 3-dimensional part, all machines have a support plate for printing the part and a nozzle or print head that moves in a plane to print the material.
The machine therefore prints in a single plane at each stage and it is the stacking of these plans which creates the volume of the printed part.
Note: For processes using UV or laser light, the printhead is usually stationary.
The main types of 3D printing
FDM
The most popular process is FDM for Fused Deposition Modeling, which involves depositing a molten plastic filament on the printing medium or on the part being printed.
A nozzle moving in a plane extrudes a hot plastic filament which, when deposited molten, welds to the previous layer.
Most consumer 3D printers use this process. Using PLA or ABS type plastics, they allow rapid prototyping or the production of functional parts for DIY, decoration or model making.
Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WHO6G67GJbM
Find the ranking of the 10 best FDM printers 2016 on this article.
SLA
This process is starting to reach the general public with printers like the 1200 Project or the Formlab which, if they are intended for the professional sector, are also affordable for individuals.
This SLA process for StereoLithography Apparatus combines a liquid photosensitive resin with an UltraViolet beam of light to solidify the resin.
With each printing layer, the machine exposes liquid resin to UV which then solidifies and welds to the previous layer of resin.
This process has been used in the dental and jewelry sector for several years now.
Find the ranking of the 10 best SLA printers 2016 on this article.
SLS
This process is still confined to the industrial sector because it involves significant implementation and costs for an individual.
This SLS process for Selective Laser Sintering uses a laser to melt a powder which, by melting, will weld itself to the previous layer.
This technology makes it possible to work with both wax and metals, and the industry's first functional metal parts are manufactured by this process.
Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bgQvqVq-SQU
How is a 3D printing machine controlled?
Unlike machining centers used in industry, 3D printers are not controlled, they operate exclusively autonomously.
The part to be manufactured is first modeled with CAD software.
The 3D file of the part is then processed by "slicing" software which will cut our part into slices, each slice representing a different section view of the modeled part.
Obviously, the more layers of printing there are, the better and smoother the surface condition of the part will be.
This STL file is then sent to the 3D printer which will successively print all the slices of the part to arrive at the complete physical model.
The 3D printing process in images example in jewelry
The production of part by the 3D printing process begins with the computer modeling of a model.
In this case, it is a ring modeled by CAD software. 
Virtual photo and CAD views of the ring
The 3D model of our ring is saved in STL format before being sent to a 3D printer interface software.
This software makes it possible to position the part on the printing plate of the machine and to set up the printing supports of the part. You can choose the position of the part on the print bed and set the number, size and location of print media.
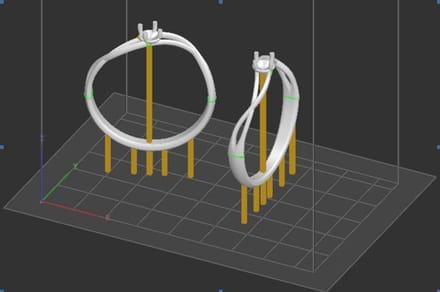
Visualization of our part on the print bed in the printer interface software.
This software for controlling the 3D printer will cut the environment of the printing plate (the parts and their supports) into slices and send them to the 3D printing machine which will print them successively.

View of the resin model printed by 3D printing.
The printed part is then detached from its supports to continue the manufacturing process that corresponds to it.
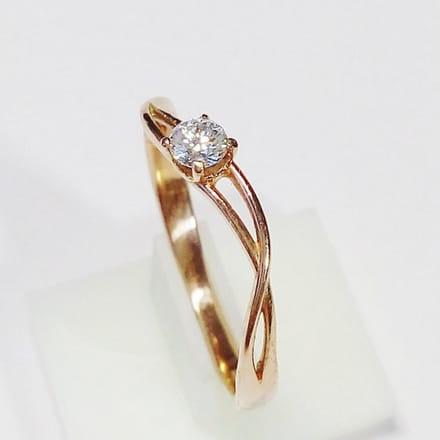

View of the finished product made from the 3D printed master.
The costs of a 3D printer
When buying a 3D printer, the machine price comparison should not be limited to the purchase price. These printers require consumables which can be expensive and have hidden costs not visible during purchase.
As for FDM type printers for example, although they use affordable raw materials, refill cartridges can be resold much more expensive than the market price by the manufacturer, which limits the possibility of being supplied via a another supplier by integrating electronic chips into the cartridge according to the same principle as the ink cartridges of traditional printers.
For FDM type 3D printers, remember to check that the machine accepts materials from a third-party supplier, and compare the price per kilo of refills depending on the printer models.
For SLA type printers, the cost of the resins can vary from 200 to 1300 euros per liter depending on the leisure or professional use of these resins. Here again, some manufacturers force their customers to use their resin by integrating a chip on the machine refills.
A printer like Formlab is betting on accepting resins from third-party suppliers to build its success (source photo).
On the other hand, the formlab requires to regularly change the printing tank which generates a cost whereas the 1200 project, by the use of interchangeable cartridges avoids this.
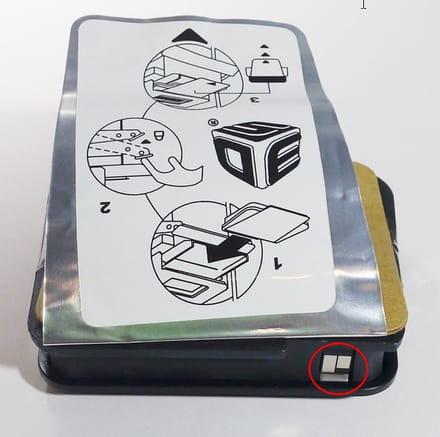
photo showing a 1200 project printer cartridge with its electronic chip (photo source)
Thanks to Nicolas Tranchant, professional 3D printer user and manager of the Vivalatina jewelry store for this article.
Thumbnail photo credit: scanrail / 123RF Image bank